3D Printing in Healthcare: Top Applications and Trends
Posted on Tue 12 August 2025 in Health
Reader Question
"What's the current state of 3D printing technology in healthcare? What are the top things being 3D printed?"
The current state of 3D printing technology in healthcare is a transformative force, offering personalized, efficient, and cost-effective solutions that are enhancing patient care and outcomes. This technology is advancing rapidly, with applications across various medical domains, and is expected to continue evolving, playing a crucial role in reshaping the healthcare landscape.
Top Applications of 3D Printing in Healthcare
- Prosthetics and Implants:
-
Customized prosthetics and implants are being 3D printed to better fit individual patients, enhancing functionality and comfort. Materials such as titanium and nylon are commonly used, offering strength and compatibility with the body. For example, the FDA has approved 3D-printed prosthetic hands [https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/3d-printing-medical-devices/medical-applications-3d-printing].
-
Anatomical Models:
-
Surgeons use detailed 3D models of organs and tissues, created from CT scans or MRI data, to plan complex surgeries. These models aid in visualization and training, improving precision and reducing risks. They are particularly useful in complex procedures, as mentioned by Carepatron [https://www.carepatron.com/nl/blog/the-impact-of-3d-printing-in-healthcare].
-
Bioprinting:
-
This emerging technology involves printing living tissues using layering techniques with living cells. While still in its early stages, bioprinting holds potential for creating tissues and organs for transplants, addressing organ shortages. However, challenges like cell viability and functionality remain, as discussed on LinkedIn [https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/future-organ-transplants-3d-bioprinting-regenerative-medicine-vvsue].
-
Pharmaceuticals:
-
3D printing is used to create pills with specific release mechanisms, offering tailored drug delivery. This approach can improve efficacy and reduce side effects, as detailed in the International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research [https://www.ijpsjournal.com/article/A+Review+On+3D+Printing+Technologies+for+Drug+Delivery+in+Pharmaceuticals+].
-
Dental Applications:
-
Custom dental products like dentures, crowns, and orthodontic models (e.g., Invisalign) are printed for precise fits. This application is well-established, with companies like Align Technology utilizing 3D printing for custom aligners [https://www.auamed.org/blog/student-research/3d-printing-in-medicine/].
-
Surgical Guides and Instruments:
-
Tailored guides and tools enhance surgical accuracy, particularly in complex procedures. These are often made from patient data, ensuring a personalized approach, as noted by the FDA [https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/3d-printing-medical-devices/medical-applications-3d-printing].
-
Tissue Engineering Models:
- These models are used to develop and test artificial tissues, aiding in drug development and tissue repair research. They provide insights into tissue mechanics and drug interactions, as discussed in the AJPRD journal [https://ajprd.com/index.php/journal/article/view/1340].
Market Growth and Regulatory Landscape
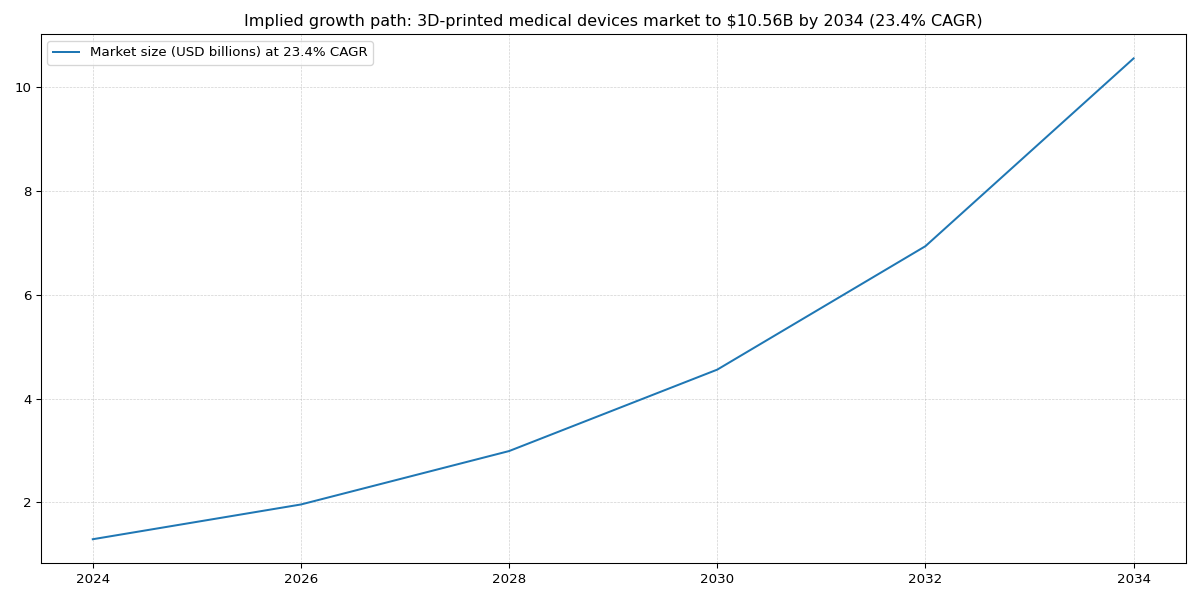
The global market for 3D-printed medical devices is growing significantly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.4%, projected to reach $10.56 billion by 2034. This growth is driven by factors such as an aging population and the demand for personalized healthcare [https://www.forinsightsconsultancy.com/reports/3d-printed-medical-devices-market].
Regulatory bodies like the FDA provide guidelines for 3D-printed devices, ensuring safety and efficacy. While these frameworks are evolving, challenges like material limitations, high costs, and accessibility remain. Standardized global regulations are still in development, as discussed in PMC [https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6140256/].
Future Prospects and Challenges
The future of 3D printing in healthcare is promising, with potential advancements in bioprinting and personalized medicine. However, challenges such as material durability, cost, and accessibility must be addressed. Despite these hurdles, 3D printing's versatility and ability to revolutionize healthcare make it a field of immense potential.
In conclusion, 3D printing in healthcare is a rapidly advancing field with diverse applications, offering customization and efficiency that enhance patient outcomes. While challenges exist, the potential for innovation, particularly in bioprinting and personalized treatments, positions this technology as a transformative force in global healthcare.
Research Statistics: - Websites Visited: 430 - Chunks Analyzed: 13,719 - Total Characters Read: 15,121,027